Components of a Circuit
All Circuits require the following Components: Power source, Protection Device, Control Device, Load, Conductors and Ground.
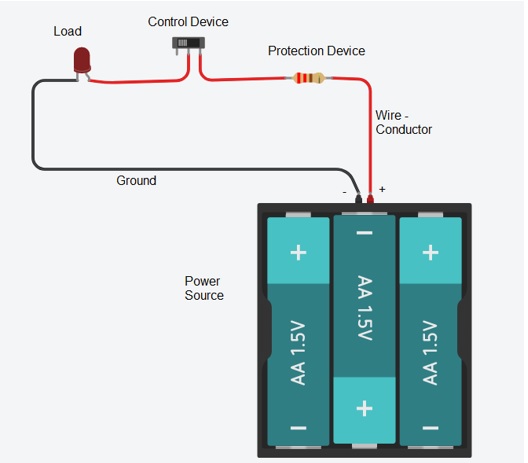
Power Source: A power source is a source of Power to the circuit. Most commonly the type of power referred to is battery. All electronic projects need a source of electrical power. This supplies the charged electrons which make electronic circuits work.

Protection Device: Protection device is required to protect the circuit from excessive current and voltages. Excessive current generates heat can damage wires and electronic components. Fuses and Fusible links can protect circuits by opening the circuit path when there is too much current. A Varistor or VDR (voltage dependent resistor) is used to protect the circuits from excessive voltages.

Fuse used to protect the circuit from over current.
MCBMiniature Circuit Breaker - It automatically switches OFF electrical circuit during overload & short circuit conditions.
MOV Metal Oxide Varistor - used to protect the circuit from high voltage spikes by varying its resistance.
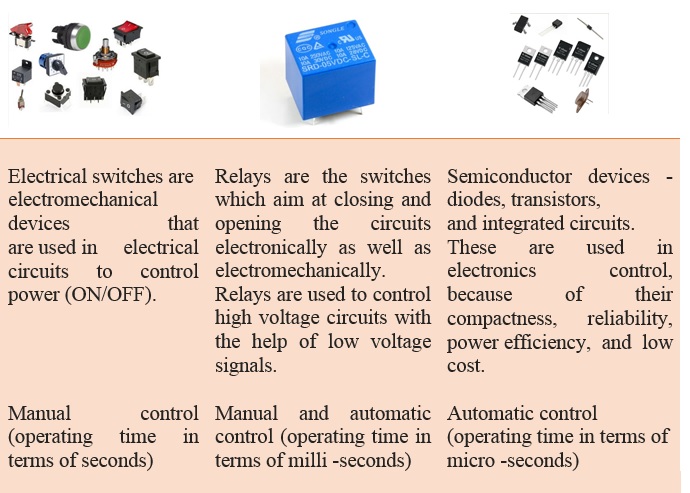
Control Device: Control in device is used to regulate the operation of a circuit, apparatus, or system. The simplest control device is as switch. A control can do more than just turn the load on and off. It can also regulate the load by varying the current.
Load: The reason we want to build circuits is to make electricity do useful things for us. The way we do that is by putting things in the circuit that use the current flow to light up, make noise, run programs, etc. These things are called loads, because they “load down” the power supply, just like you're “loaded down” when you're carrying something.

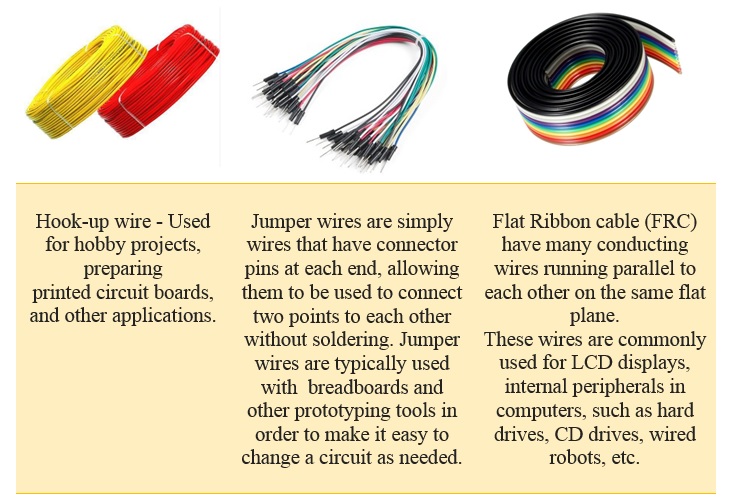
Conductors: Conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow through them. Conductors are used to inter-connect the electronic components.
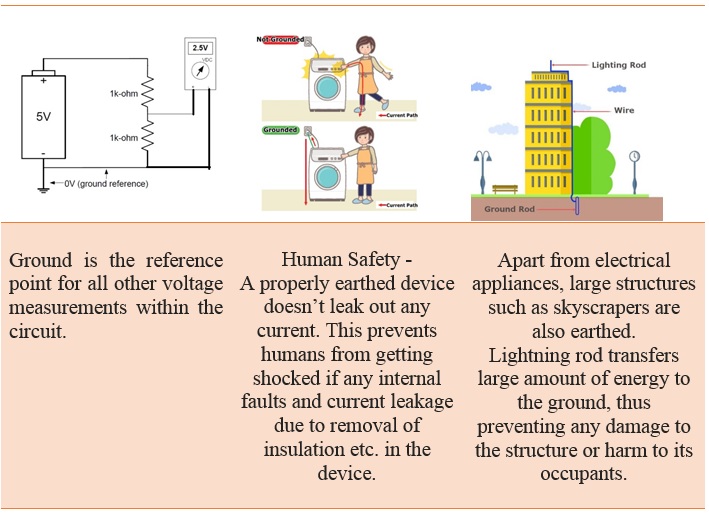
Ground: In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the earth.