Electrical Control switch - Relay
Relay is an electromechanical switching device most widely used in the automotive and telecommunication industries. It can be found in cars, washing machines, medical equipment, aircraft, etc. We can see that relays are being used in control systems and power systems industries to protect the system or load circuit from unexpected damage.
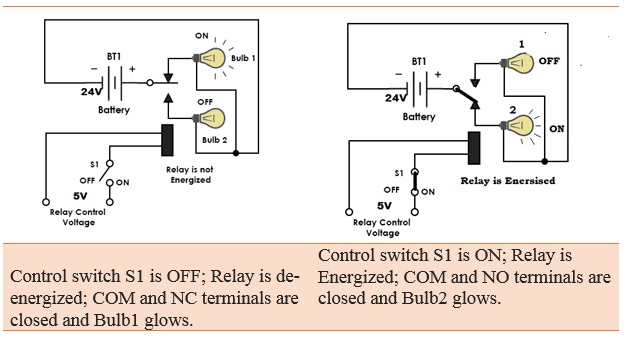
A switch is a component that opens (turn off) & close (turn on) an electrical circuit manually. whereas, a relay is an electrical switch that control (switch on & off) a high voltage circuit using a low voltage source. A relay completely isolates the low voltage circuit from the high voltage circuit. Relays can be controlled electronically. Relay operates faster than switches.
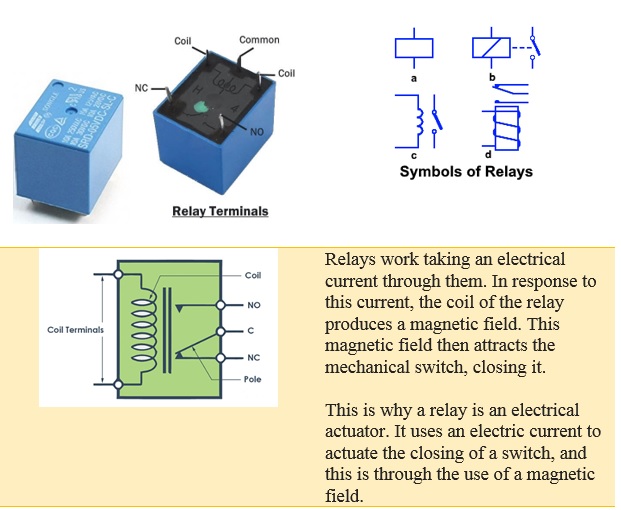
Terminals of a Relay
Control Input or Coil Terminals:
Control input terminals are two input terminals of a relay that controls its switching mechanism. A low power source is connected to these terminals to activate & deactivate the relay.
NO Terminal:
NO or Normally Open terminal is also a load terminal of a relay which remains open when the relay is not active.
NC Terminal:
NC or Normally Closed terminal is the other load terminal of a relay. This terminal is normally connected with COM terminal of the relay when there is no control input.
COM or Common Terminal:
It is the terminal of the relay where you connect the first part of your circuit. When the relay is powered, and the switch is closed, the common terminal and the normally open terminal have continuity. On the other hand, when the relay is not powered, and the switch is open, the common terminal and the normally closed terminal have continuity.